Background: ‘At-risk’ and technological interventions
A friend and I have been having a back and forth about improving completion rates of ‘at-risk’ students in both secondary schools and in the early years of university study. By ‘at-risk’ in this scenario, I am referring to (especially in regards to the university study), students who show poor attendance records, students who have little family support or university precedent (those whose parents didn’t attend university), etc. We were discussing evidence from developing nations that could be used in developed, as well as the study suggesting that SMS (text messaging) can improve enrollment rates for low-income students. We discussed some ideas and solutions.
This one always seemed like a bit of an easy fix to me if success is defined as merely improving completion rates by x% (say, by 10-15% which is a significant improvement). It works under the assumption that SMS is an existing, widely used, socially acceptable communication channel and an ‘intervention’ built on that channel would be aligned with existing social practice. Also, there are hundreds of comparable projects on which to build a structure for at-risk students.
So the goal is not to build a new structure, a new technology, or social network or what have you, but rather the sharpest, most direct, most affordable means of intervention. Hence SMS. So the idea is as follows, presented as I wrote it. All one would need would be a willing university or school district, the curricula, schedules, and assignments for each department, and a pool of students and mentors. The technology could be housed off a laptop or, depending on the scope of activity, on a network computer. Most importantly, it would be a smart logic SMS structure, where routing triggers would indicate a particular communication (P2M (peer to mentor), P2P (peer to peer), etc. To get the students involved, they can choose the routing triggers with language that resonates to them. This is about as cheap as it is possible to make it and it scales. So, if this interests you, please find the outline below. Frontline SMS would be a free system (barring texting costs) to use to manage the activity.
SMS Communication Project to Improve Resiliency to Complete Formal Programs of Study
General Idea: When navigating new or challenging terrain, all educational theory suggests that we learn best and most resiliently through scaffolding, ie structuring activity in manageable bits to prevent overflow and disengagement (drop-out). Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development addresses this quite convincingly. So the idea here is to provide scaffolds through social interaction, either Peer to Peer, Peer to Mentor, etc. in order to build resiliency to complete formal programs of learning. The ability of the learner to complete the program of learning is not always or even primarily based on the skill that learner shows in the subject area, but rather their ability to use their community for support (emotional or academic). Social interaction is the glue that keeps students engaged.
So matching the most widely available technology (SMS) with some of the most widely available social motivators (compassion, sympathy, support) will generate improved resiliency rates. This project succeeds as it capitalizes on existing technology and existing communication structures (texting) to channel existing social motivation (community support) for community achievement (pass or complete).
Overview
Develop an SMS-based mentoring and peer support system that creates (two-way) communication channels to
- Organization to student communication
- Student to student communication
- Mentor to student communication (vice versa)
- Disciplinary communication (Department to student)
Purpose
- to increase resiliency of at-risk students for completing formal education programs
- to increase graduation rates for at-risk students at secondary school by 15%
- to increase completion of early years of university (1st-3rd years, primarily) for at-risk students or those without university precedent (ie, parents who are university graduates) by 20%
Key Design Principles
- Work with the most widely available technology (SMS)
- Understand that resiliency is an emotional context (student to student, mentor to student)
- Understand that small scale, repeated intervention is most effective (nudge, poke, reminders, encouragement)
- Understand that we all want to be sought after and found (do not doubt the resilience brought upon by sympathetic or empathetic intervention and mentoring, however low-tech)
Deliverable
- One SMS system managed from organizational ICT or from peer or mentor laptop (consider centralized vs. decentralized hosting as a factor in resiliency and participation. Peer networks, created by and for peers and mentors, are quite resilient as they are owned by the members).
- Smart logic from the communication channels at work, presented in easy to understand instructions with keyword triggers that resonate with the learners (have them create the terms)
- Sustainability plan- this project would need one full-time employee (FTE) to manage it at roughly (depending on the number of participating students and departments) 20-50% time
- Prepared schedules, curricula, assignment delivery dates-these would be pre-loaded and communicated on scheduled dates as reminders to the students based on certain routing logic
Cost
- One FTE at 50% time (ongoing)
- One laptop or network computer to host
- Development cost (time: 50 hrs of development)
- Information gathering time (requisites, assignments, routing logic, etc.)
Structure
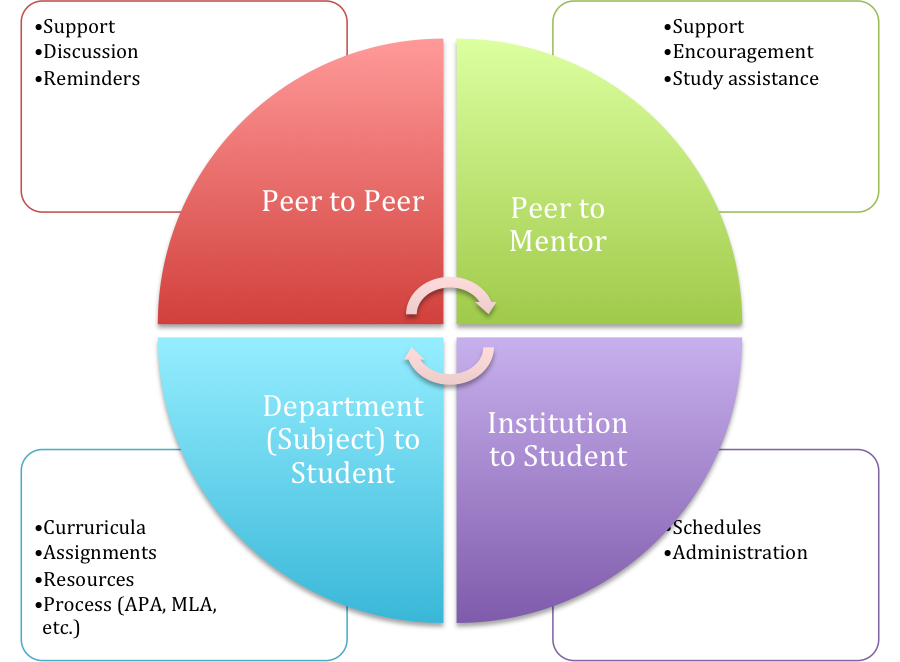
There are four discrete activities taking place via SMS in this system. Each of these would be triggered by smart logic routing rules according to the categories listed below (Peer to Peer, Peer to Mentor, etc.) For example: The P2P, P2M, M2P represents routing logic. If the student began a text with P2P, it would be routed specifically to the designated Peer group. P2M would be the mentor, etc. Examples texts are below:
- P2P Does anyone know what this teachers wants from this?
- P2M I am not sure what to do
- M2P First, consider doing this…
Background
- Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development
- Frontline SMS
- SMS Routing Logic for Support of Higher Education in East Africa
- Benefits of Texting Infographic
- Community Resiliency Theory
- Anything from Community of Practice Theory
[…] Background: 'At-risk' and technological interventions A… […]
[…] Feedback loops: developing meaningful mentoring and feedback channels for developing professional practice in the humanities via configurations of […]